The Indus Valley Civilization (IVC), one of the world’s earliest urban cultures, emerged around 250…
Read MoreThe Indus Valley Civilization (IVC), one of the world’s earliest urban cultures, emerged around 250…
Read MoreThe Vedic Civilization, which followed the decline of the Indus Valley Civilization, marks the form…
Read MoreThe Mahajanapada period (c. 600–300 BCE) marks a significant transformation in Indian political his…
Read MoreThe Mauryan Empire (321–185 BCE), founded by Chandragupta Maurya, was the first pan-Indian empire t…
Read MoreEmperor Ashoka (r. 268–232 BCE), one of India’s greatest rulers, transformed from a ruthless conque…
Read MoreThe Mauryan Empire, once the largest and most powerful political and military empire in ancient Ind…
Read MoreThe Shunga Dynasty emerged after the fall of the Mauryan Empire, marking a significant political an…
Read MoreThe Satavahana Dynasty emerged after the decline of the Mauryas, becoming a powerful political forc…
Read MoreThe Indo-Greek and Kushan invasions between the 2nd century BCE and 3rd century CE brought Central …
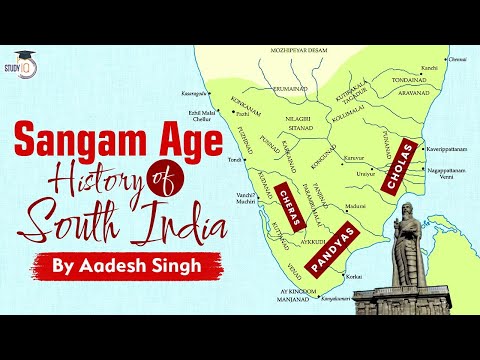
Read MoreThe Sangam Age (circa 300 BCE – 300 CE) refers to the flourishing era of Tamil literature, culture,…
Read MoreThe Mauryan Empire (c. 322 BCE – 185 BCE) was the first major pan-Indian empire, established by Cha…
Read MoreAfter the fall of the Mauryan Empire in 185 BCE, northern India saw the rise of several foreign dyn…
Read MoreThe Gupta Empire, which ruled large parts of northern and central India from the 4th to 6th century…
Read MoreThe decline of the Gupta Empire around the mid-6th century CE led to the emergence of multiple regi…
Read MoreThe Pallavas and Chalukyas were two dominant South Indian dynasties that flourished between the 6th…
Read MoreThe Rashtrakutas were a powerful dynasty from the Deccan region who ruled large parts of India from…
Read MoreThe Pandyas and Cheras were two ancient Tamil dynasties based in southern India. Known for their ex…
Read MoreAn in-depth exploration of how Chandragupta Maurya built the Maurya Empire from fragmented territor…
Read MoreA comprehensive look into Bindusara’s role in strengthening the Mauryan Empire after Chandragupta’s…
Read MoreThis blog explores the origins, establishment, and expansion of the Delhi Sultanate in India, highl…
Read MoreThis blog delves into the revolutionary market reforms and military strategies of Alauddin Khalji, …
Read MoreThis blog explores the bold and experimental rule of Muhammad bin Tughlaq, known for his visionary …
Read MoreThis blog explores the reign of Firoz Shah Tughlaq, the third ruler of the Tughlaq dynasty, focusin…
Read MoreThis blog examines the origins and rise of the Vijayanagara Empire (1336–1646 CE), one of the most …
Read MoreThis blog explores the Bahmani Sultanate (1347–1527 CE), the first independent Islamic kingdom in t…
Read MoreThis blog explores the Tughlaq Dynasty (1320–1414 CE), the third ruling dynasty of the Delhi Sultan…
Read MoreThe Vijayanagara Empire (1336–1646 CE) was one of the most powerful South Indian kingdoms that emer…
Read MoreThe Bahmani Kingdom (1347–1527 CE) was the first independent Islamic kingdom in South India, formed…
Read MoreThe Delhi Sultanate, originally based in North India, extended its influence deep into the Deccan b…
Read MoreKrishna Deva Raya, the greatest ruler of the Vijayanagara Empire (1509–1529 CE), is remembered as a…
Read MoreThe Battle of Talikota, fought in 1565 CE, was a catastrophic turning point that led to the dramati…
Read MoreThe foundation of the Mughal Empire under Babur and its survival through turbulent years under Huma…
Read MoreAkbar the Great, the third emperor of the Mughal Empire, is remembered as one of the most visionary…
Read MoreJahangir and Shah Jahan, successors of Akbar, continued the legacy of the Mughal Empire through pol…
Read MoreAurangzeb Alamgir, the sixth Mughal emperor, was a devout orthodox ruler whose reign marked the emp…
Read MoreAfter Aurangzeb's death in 1707, the Mughal Empire entered a prolonged phase of decline. Successors…
Read MoreThe Maratha Confederacy emerged as a dominant political and military force in 18th-century India. B…
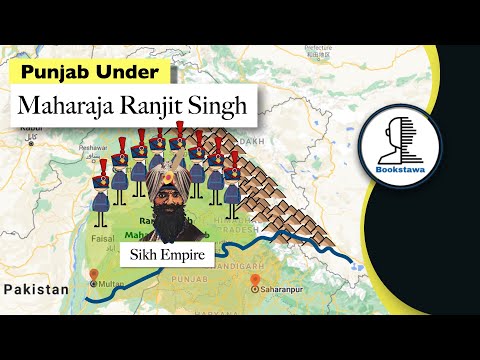
Read MoreThe Sikh Empire under Maharaja Ranjit Singh was a rare example of a powerful and secular indigenous…
Read MoreThe Bhakti and Sufi movements, emerging in medieval India, transformed the spiritual and cultural l…
Read MoreThe Mughal Empire established one of the most sophisticated and centralized administrative systems …
Read MoreThe emergence of the Marathas as a dominant force in 17th-century India changed the course of subco…
Read MoreAfter Shivaji’s death, the Maratha Empire evolved into a powerful confederacy under the leadership …
Read MoreThe Third Battle of Panipat, fought in 1761 between the Marathas and Ahmad Shah Abdali’s Afghan arm…
Read MoreThe Mughal Empire, once the most powerful and wealthy empire in India, began to disintegrate in the…
Read MoreThe British came to India as traders under the East India Company but eventually transformed into r…
Read MoreThe Revolt of 1857 marked a significant uprising against British colonial rule in India. Though it …
Read MoreThe 19th century in India witnessed a wave of social reform movements aimed at eradicating regressi…
Read MoreThe formation of the Indian National Congress (INC) in 1885 marked a historic milestone in India’s …
Read MoreThe partition of Bengal in 1905 by Lord Curzon marked a turning point in India's freedom struggle. …
Read MoreThe Surat Split in 1907 marked the ideological division within the Indian National Congress between…
Read MoreLaunched during World War I, the Home Rule Movement was a significant phase in India’s freedom stru…
Read MoreThe Lucknow Pact of 1916 was a landmark agreement between the Indian National Congress and the All-…
Read MoreThe Montagu-Chelmsford Reforms, legislated through the Government of India Act, 1919, were a signif…
Read MoreLaunched by Mahatma Gandhi in response to the Rowlatt Act, Jallianwala Bagh massacre, and Khilafat …
Read MoreThe Simon Commission (1927) was a British initiative to review constitutional progress in India but…
Read MoreThe Lahore Session of the Indian National Congress in 1929, presided over by Jawaharlal Nehru, mark…
Read MoreThe Civil Disobedience Movement, launched by Mahatma Gandhi in 1930, was a nationwide campaign of n…
Read MoreThe Round Table Conferences, held in London between 1930 and 1932, were an ambitious attempt by the…
Read MoreThe Government of India Act, 1935 was the most extensive constitutional reform introduced by the Br…
Read MoreThe Quit India Movement, launched in August 1942, was one of the most intense and widespread mass m…
Read MoreThe Indian National Army (INA), led by the charismatic Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose, aimed to overthr…
Read MoreThe Royal Indian Navy Revolt of 1946 was a spontaneous uprising by Indian naval ratings against Bri…
Read MoreThe Mountbatten Plan, announced in June 1947, was the last official blueprint that led to the Parti…
Read MoreAfter Independence in 1947, one of India's biggest internal challenges was integrating over 560 pri…
Read MoreAfter centuries of colonial rule, India not only had to gain independence but also establish a demo…
Read MoreThis blog delves into the Nagara style of temple architecture, one of the major schools of temple d…
Read MoreThis blog explores the Dravida style of temple architecture, a prominent form that developed in Sou…
Read MoreMaharishi Dayanand Saraswati (1824–1883), a revolutionary social and religious reformer of 19th-cen…
Read MoreFounded by Maharishi Dayanand Saraswati in 1875, the Arya Samaj emerged as a powerful socio-religio…
Read MoreIndia's Intangible Cultural Heritage (ICH) embodies the spirit of the nation’s living traditions—ri…
Read MoreIndia’s tribal art and culture represent some of the oldest and most vibrant living traditions in t…
Read MoreThe Sufi and Bhakti movements, which emerged in medieval India, played a pivotal role in shaping th…
Read MoreAncient India made monumental contributions to science and mathematics long before the emergence of…
Read MoreRock-cut architecture in India represents one of the most remarkable forms of structural ingenuity,…
Read MoreIndia’s strategic location between the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal turned it into a maritime …
Read MoreThe position of women in ancient India evolved drastically from the Vedic period to the post-Vedic …
Read MoreBuddhism, originating in India, spread far beyond its birthplace and left a profound impact on the …
Read MoreRaja Ram Mohan Roy was a visionary reformer and intellectual who laid the foundation of modern Indi…
Read MoreSwami Vivekananda was a towering spiritual leader and a key figure in India's cultural and national…
Read MoreSwami Dayananda Saraswati (1824–1883) was a fearless social and religious reformer of 19th-century …
Read MoreIshwar Chandra Vidyasagar (1820–1891) was a pioneering educationist, reformer, writer, and humanist…
Read MoreSri Ramakrishna Paramhamsa (1836–1886) was a mystic saint, spiritual teacher, and a key figure in t…
Read MoreRani Lakshmibai (1828–1858), popularly known as the Queen of Jhansi, remains one of the most iconic…
Read MoreDr. Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar, a visionary social reformer, jurist, economist, and the principal archi…
Read MoreJyotirao Govindrao Phule was a fearless social reformer, educationist, and thinker who laid the fou…
Read MoreGopal Krishna Gokhale was one of the most influential political leaders and social reformers of the…
Read MoreBal Gangadhar Tilak was one of the most dynamic and influential leaders of the Indian independence …
Read MoreAnnie Besant, a British socialist, theosophist, and orator, played a pivotal role in India's socio-…
Read MoreDadabhai Naoroji was a pioneering nationalist leader, educator, and economic thinker who laid the i…
Read MoreGopal Krishna Gokhale was a visionary Indian political leader, social reformer, and moderate nation…
Read MoreBal Gangadhar Tilak was one of the most influential leaders of India’s early nationalist movement. …
Read MoreBhagat Singh was one of India's most iconic revolutionary freedom fighters, remembered for his fear…
Read MoreLala Lajpat Rai, often referred to as the “Punjab Kesari” (Lion of Punjab), was one of the most pro…
Read MoreRobert Clive, also known as Clive of India, was a British military officer and colonial administrat…
Read MoreWarren Hastings was the first Governor-General of Bengal and later of all British India (1772–1785)…
Read MoreLord Cornwallis, the second Governor-General of India (1786–1793), is remembered primarily for his …
Read MoreLord Richard Wellesley, Governor-General of India from 1798 to 1805, played a pivotal role in expan…
Read MoreTipu Sultan, the ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore (1782–1799), was one of the fiercest opponents of B…
Read MoreThe civil services in India have evolved from a colonial instrument of control under the British Ra…
Read MoreThe Champaran Satyagraha of 1917 marked Mahatma Gandhi’s first active intervention in Indian politi…
Read MoreChoose an option to continue: